
If the connection is working properly you will see something That the printer is properly connected to your LAN, type: ping ip-address To test that the IP address has been successfully assigned and The /etc/nf or /etc/xinetd.d/bootp file usually contains a line for the BOOTP service that can be uncommented if needed. Note: Some versions of UNIX do not enable the BOOTP service by default. If you do not need to provide a boot file you may leave the last part of the line blank. The myprinter.boot file resides in the /usr/local/boot directory by default. Newer versions of bootpd use a different format:
Using the standard bootpd(8) program supplied with UNIX you simply need to add a line to the /etc/bootptab file for IRIX: The BOOTP protocol is used when you need to provide additional information such as the location of a configuration file to the network interface. Make sure that the hostname you use is also listed in the /etc/hosts file or is registered with your DNS server. Using the standard dhcpd(8) program supplied with UNIX you simply need to add a line to the /etc/nf file: The DHCP protocol is the usual way of setting the IP address of a printer on a managed network. The Ethernet MAC address can often be found on the printer test page or bottom of the print server. To setup your printer or print server for remote address assignment, you'll need the Ethernet Media Access Control ("MAC") address, also sometimes called a node address, and the IP address you want to use for the device. However, if you have many printers you will want to assign the addresses remotely - this makes administration a bit easier and avoids assigning duplicate addresses accidentally. Most higher-end "workgroup" printers allow you to set the address through the printer control panel. When you first install a network printer or print server on your LAN, you need to set the Internet Protocol ("IP") address. The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can also be used to get the IP address remotely, which happens automatically when you visit the CUPS administration web page or choose an available CUPS device when adding a printer.

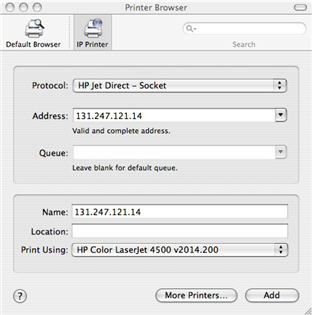
You can normally find the IP address of a printer on the printer's control panel or by printing the configuration or status page. This address is either configured manually or set using an automatic network protocol such as the Boot Protocol (BOOTP), Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP), Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP), or ZeroConf. Getting the IP AddressĮvery network printer or print server has a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address associated with it.
This help document describes how to discover, configure, and use TCP/IP network printers with CUPS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
